A rare new explosion will soon be visible in Earth’s night sky, according to NASA officials.
The event, which could happen anytime between now and September, is causing a stir in the astronomy community as both professional and amateur astronomers will be able to see the explosion.
“We’re definitely seeing a lot of excitement as sky watchers await the predicted nova,” Claire Andreoli, manager of astrophysical communications at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, told Yahoo News. “We rarely get the opportunity to witness something like this with our own eyes, which definitely adds to the buzz.”
🌟 What makes a star new?
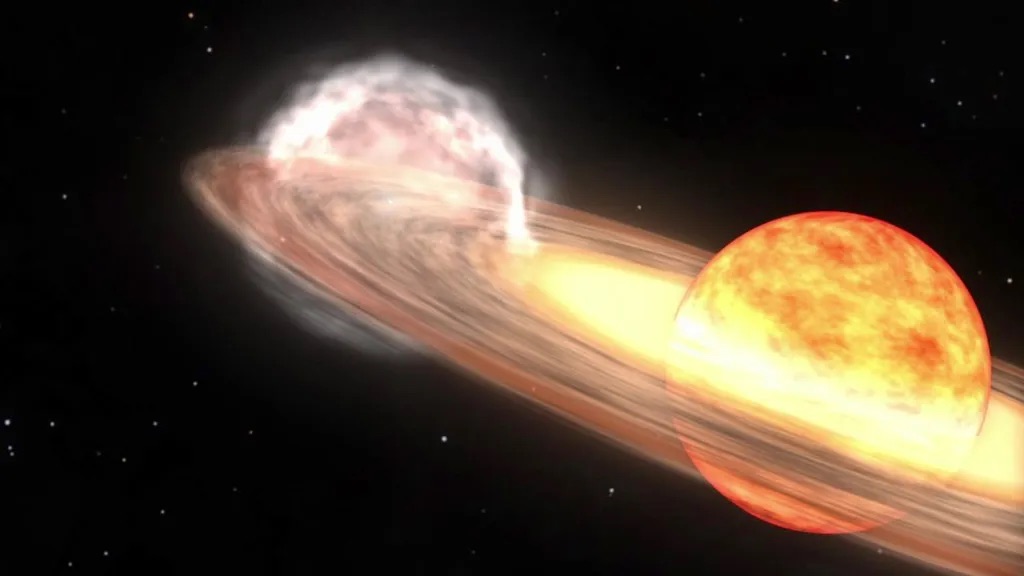
Located 3,000 light-years from Earth, T Coronae Borealis (T CrB), nicknamed the Flaming Star, is a binary star system in the constellation Coronae Borealis (or “Northern Corona”).
In this binary system, a white dwarf (a dead star) and an ancient red giant (a slowly dying star) are gravitationally bound to each other. Every 80 years or so, the hydrogen from the red giant fuses with the surface of the white dwarf, causing pressure and heat to build up, resulting in a fusion explosion, causing the system to become nova.
The last time a new T CrB was seen from Earth was in 1946.
💥 What is the difference between a nova and a supernova?
A nova is an astronomical event in which a star experiences a sudden and dramatic increase in brightness – sometimes up to 100,000 times its normal level.
This results in the appearance of a “nova” star in the night sky (“nova” is the Latin word for “new”), which slowly fades over weeks or months.
A nova differs from a supernova in that during a new star it flares up, then goes back into dormancy. In a supernova, the star is completely destroyed.
🌌 Around the world, professional astronomers and amateurs are closely watching T Coronae Borealis – a binary system ~3000 light years from Earth – in anticipation of an upcoming new event so bright that it will be visible on Earth with the naked eye.
MORE HERE >> https://t.co/HgONmjpy9B pic.twitter.com/L54ZDFmFWA
— NASA Marshall (@NASA_Marshall) June 6, 2024
“T CrB is a once-in-a-lifetime event,” Dr. Rebecca Hounsell, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, told Yahoo News. “This event will inspire a new generation of astronomers as everyone can participate in observing this amazing astronomical event.”
📍How to find T Coronae Borealis in the night sky
When T CrB becomes new, it will be visible to the naked eye for about a week.
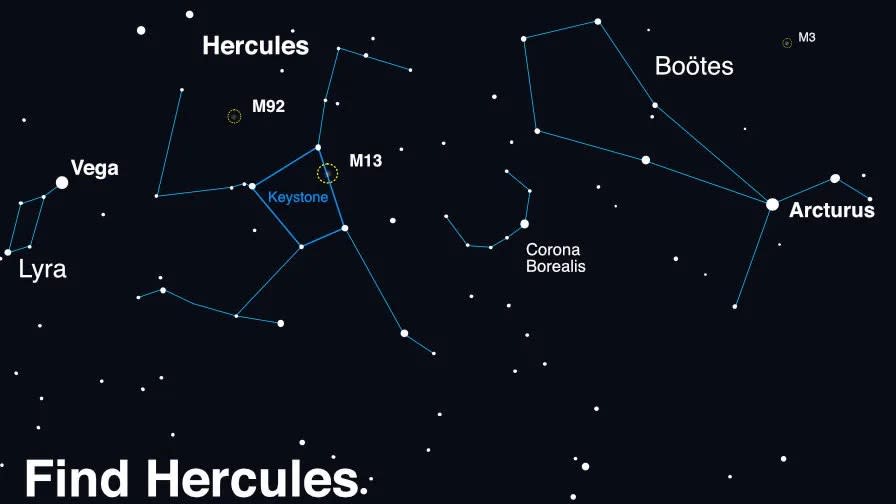
To see it, first find the constellation Hercules, then look west for the Northern Crown, a horseshoe-shaped curve of stars.
“[The Northern Crown] can be identified by locating the two brightest stars in the Northern Hemisphere – Arcturus and Vega – and tracing a straight line from one to the other, which will take sky watchers to Hercules and Corona Borealis,” NASA says on its website .
“This will be a fleeting event and may be difficult to detect,” Andreoli told Yahoo News.
“We’re really trying to manage expectations and give people as much information as possible so that hopefully they’re ready to witness this incredible space spectacle.”
💡How best can you see the nova
-
Avoid light pollution. Light pollution is scattered light from parking lots, sports complexes, street lighting, and other human activity that manifests itself as a glow in the night sky. For darker skies, head at least 20 to 30 miles from city limits, NASA advises.
-
Check the weather forecast. Make sure it’s a clear, cloudless night with good transparency (low dust and humidity levels). Websites like Good to Stargaze can tell you if the forecast for your location is favorable for stargazing.
-
Use a constellation or planisphere app. Apps like Sky Guide use AR technology to turn your phone into a map to the stars. For those who prefer a more hands-on guide, a planisphere can help you find the constellation Hercules.



