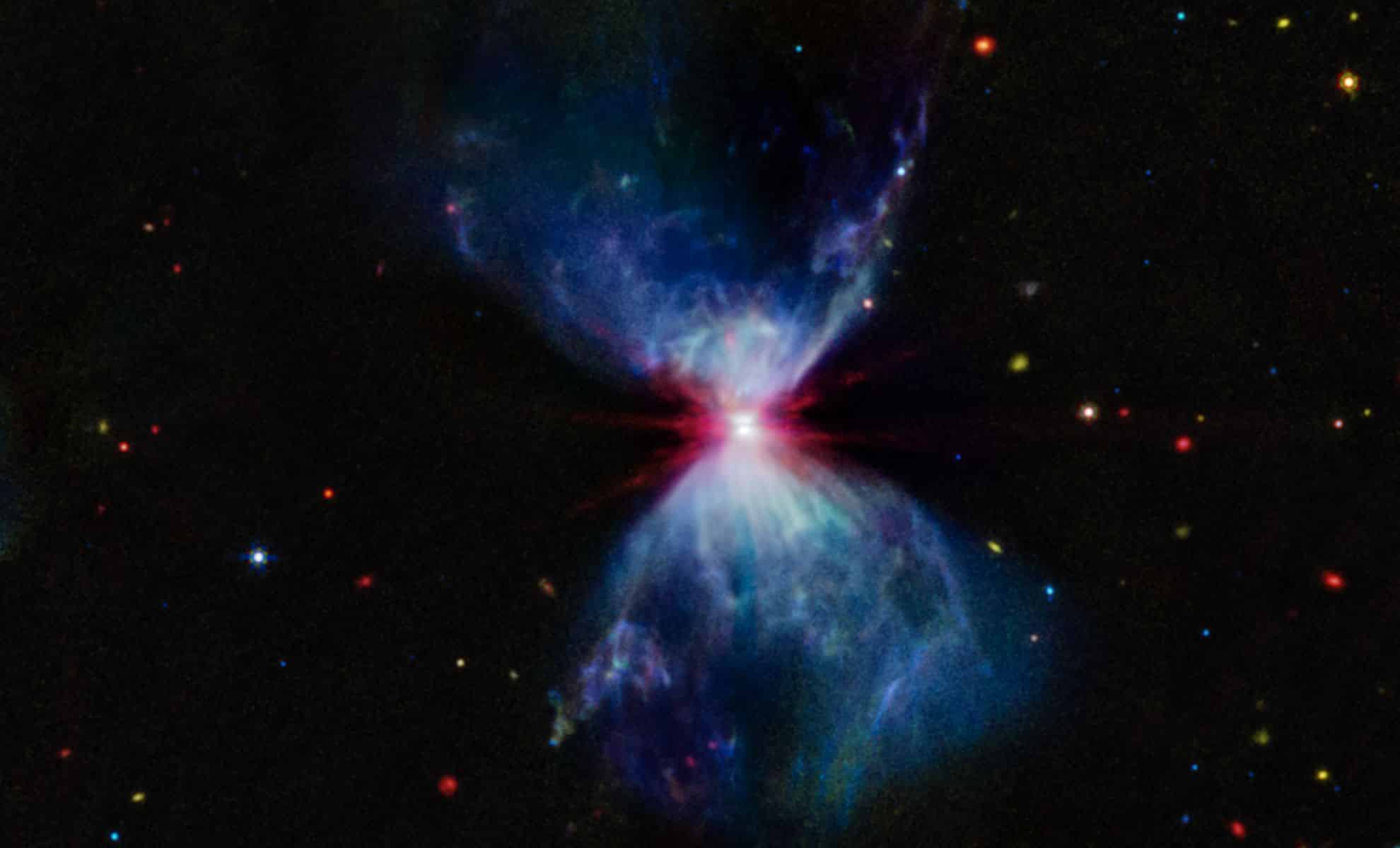
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) provided a breathtaking glimpse into the early stages of star formation, capturing the dramatic development of a protostar in an hourglass-shaped luminous cloud.
This observation, which highlights the complex processes involved in star birth, offers deep insight into the behavior and evolution of young stellar objects.
Observation of Protostar L1527
At the center of this remarkable observation is protostar L1527, nestled in the dark molecular cloud known as L1527. Using JWST’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), scientists obtained a vivid image showing the protostar as it underwent significant changes.
This protostar, about 100,000 years old, is in the early stages of star formation, actively accreting material from the surrounding protoplanetary disk. The striking hourglass shape captured in the image is the result of powerful outflows emitted by the protostar interacting with the surrounding molecular cloud.
Details revealed by Mid-Infrared Imaging
The MIRI image offers a detailed look at the protostar and its environment, revealing several critical features. At the hourglass core, the protostar is surrounded by a dense protoplanetary disk, visible edge-on as a dark line.
As the protostar accretes material from this disk, it emits outflows that collide with the surrounding molecular cloud, creating shocks. These interactions produce filamentary structures that illuminate the hourglass shape, providing a dynamic snapshot of star formation in action.
The role of gas and dust
The mid-infrared image from MIRI provides unique insight into the composition of the protostar’s environment. The image distinguishes between different materials, with blue regions indicating the presence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and red regions representing the dense dust and gas surrounding the protostar.
This differentiation helps scientists understand how the protostar’s outflows affect and change the surrounding molecular cloud, shedding light on the complex interactions that occur during the early stages of star formation.
The future of the protostar
As the protostar continues to evolve, it will absorb and scatter much of the surrounding material. Energy jets and outflows will eventually clear the molecular cloud, making the star more visible in the future.
This process, observed in detail by JWST, sheds light on the early stages of star formation and the dynamic interactions between young stars and their natal environment.
Implications for star formation
Detailed observations of L1527 provide significant insight into star formation mechanisms. The interaction between the protostar outflows and the molecular cloud not only shapes the immediate environment, but also influences the formation of other stars in the region. This dual role can either prevent or catalyze the birth of new stars, depending on the particular conditions.
Impacts on the surrounding region
As the protostar matures, its continued interaction with the molecular cloud will have wider consequences for the surrounding region. The outflow and energy jets from L1527 may affect the formation of other stars nearby, either by compressing the surrounding material to trigger new star formation, or by dispersing the gas and dust, thus preventing the birth of additional stars. These observations provide insight into the dynamical processes that govern star formation and the evolution of stellar nurseries.
The role of the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope, a joint effort between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), continues to push the boundaries of our understanding of the universe. By observing celestial phenomena such as the formation of protostar L1527, JWST provides invaluable data that helps unravel the complexities of cosmic evolution.
Future studies and findings
The findings from this observation not only improve our knowledge of star formation, but also pave the way for future research that will further illuminate the processes that govern the birth and development of stars in our galaxy and beyond. As JWST continues its mission, it promises to reveal more secrets of the universe, contributing to our understanding of the fundamental processes that shape the cosmos.