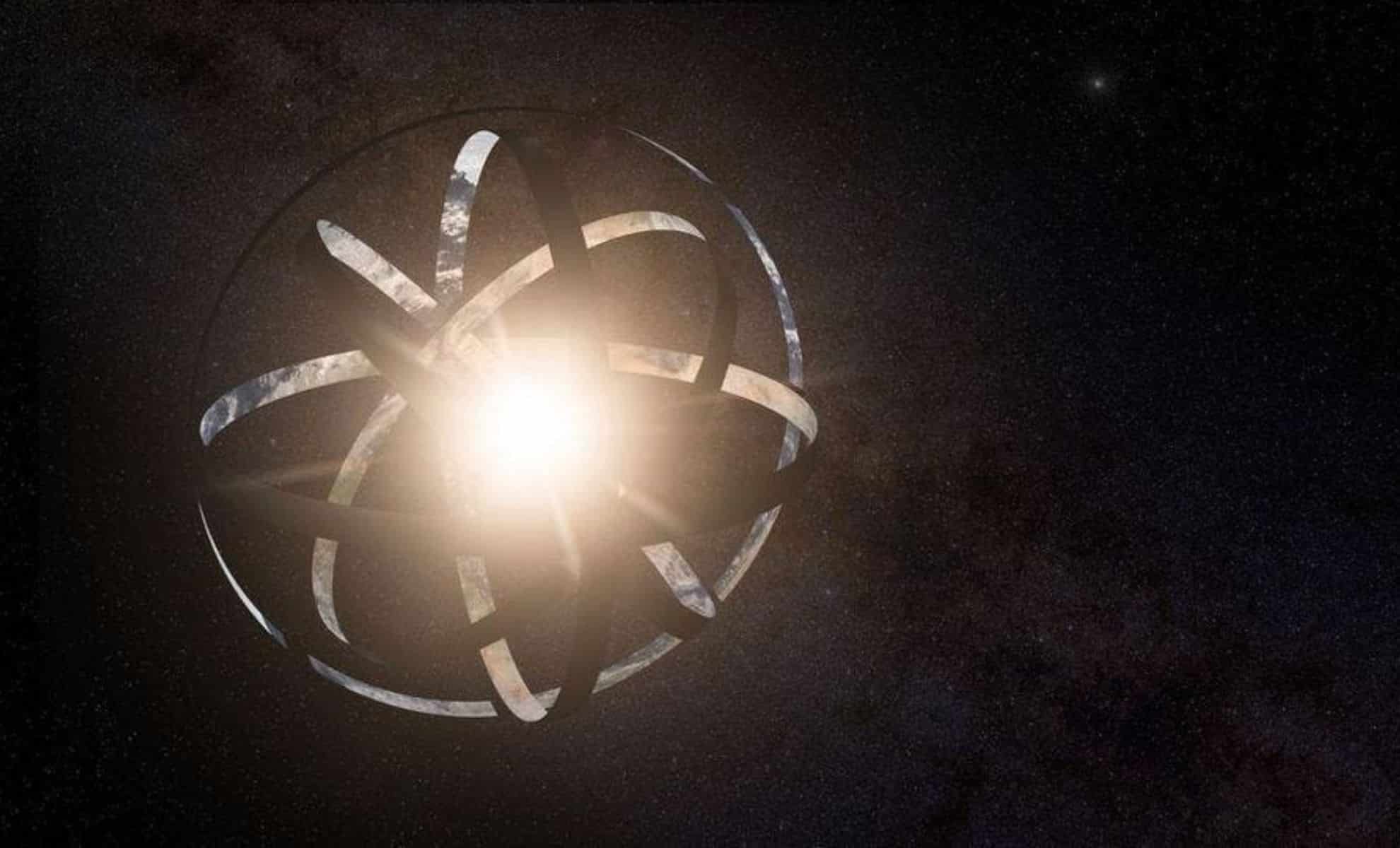
Recent studies have sparked renewed interest in the concept of Dyson spheres, theoretical megastructures that could potentially harness the energy of entire stars.
This intriguing idea has led some scientists to speculate whether such structures could explain the universe’s missing mass. Despite the excitement, however, many experts remain skeptical about the existence of Dyson’s spheres and their role in explaining astronomical phenomena.
The concept of Dyson spheres
The idea of Dyson spheres was first proposed by a physicist Freeman Dyson in 1960, inspired by the sci-fi novel Starmaker by Olaf Stapledon. Dyson hypothesized that an advanced extraterrestrial civilization could build huge structures around their stars to capture solar energy.
These structures, while blocking visible light from the star, would emit infrared radiation, potentially making them detectable by astronomers. “It’s possible to just play regular old astrophysics,” said astrophysicist and science writer Dr. Ethan Siegel, stressing the need for extraordinary evidence to support the existence of such megastructures.
The concept gained considerable attention with the discovery of mystery star KIC 8462852, also known as Boyajian’s star, which shows irregular and significant dips in brightness. Some have speculated that they may be caused by an incomplete Dyson sphere, although this remains unconfirmed.
Missing mass in the universe
Astronomers have long been puzzled by missing mass in the universe. There are two types of missing mass: dark matterwhich is necessary to explain the gravitational behavior of galaxies, and regular questionprimarily composed of hydrogen and helium, which appears to be in short supply based on current observations.
While dark matter thought to consist of exotic particles, the missing normal matter remains a mystery. Some suggest that vast filaments of gas stretching between galaxies may account for this.
Can Dyson Spheres Explain Missing Mass?
Despite the charming nature of Dyson Spheres, they are unlikely to explain the missing mass in the universe. Complete Dyson spheres, which would completely surround a star, are considered impractical due to the enormous amount of material required and the gravitational instability such structures would face.
Even if they were constructed, these spheres probably would be very thin and unstable, which makes them implausible. They are more believable Dyson swarms or rings, networks of solar-harvesting satellites orbiting a star. These structures would capture only a fraction of the star’s light, making them easier to build, but much less likely to account for the missing mass. Furthermore, if such swarms are common, their infrared radiation should be detectable by telescopes such as James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). However, no evidence has been found to suggest that they are widespread.
Recent observations and skepticism
A recent study published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society reported on opening seven stars with unusual infrared signatures potentially indicative of Dyson spheres. These stars, located within 1,000 light-years from Earth, show heat signatures that cannot yet be fully explained.
However, many experts remain skeptical. Dr. Janna Levine, a theoretical cosmologist at Barnard College, suggested that these signatures could be due to natural astrophysical phenomena such as collisions of planets or young stars with the surrounding material. “Heat signatures are so general in nature that they are far from smoking guns, and there are many possible natural explanations,” Levin told Salon.
Astrophysicist Dr. Eric Zakrisson, one of the study’s co-authors, echoed that skepticism, noting that while these stars are the best candidates for Dyson Spheres so far, other explanations such as dust from cosmic events or background sources are also plausible. “They’re the best Dyson sphere candidates we’ve come across so far, but that doesn’t mean they’re Dyson spheres, or even that Dyson spheres represent the most likely explanation for the phenomenon we’re seeing,” Zakrisson said.
The scientific value of search
Despite doubts, the search for Dyson Spheres has considerable scientific value. It encourages the exploration of unconventional ideas and encourages interdisciplinary research combining astrophysics, history and other fields. The potential discovery of extraterrestrial megastructures would be a groundbreaking achievement, transforming our understanding of the universe and the existence of advanced extraterrestrial civilizations.
“What could be more exciting and existentially terrifying than the discovery of extraterrestrial life?” Levin mused, stressing the importance of remaining open-minded while maintaining scientific rigor. Dr. Siegel added, “It’s important to keep an open mind, and it’s easy to see why even the wildest possibilities excite us. But without more solid evidence, this is just another example of people getting excited about what will almost certainly be a big nothing-burger.”
In conclusion, while Dyson Spheres remain a fascinating theoretical concept, their existence as a solution to the missing mass of the universe is highly unlikely. However, the ongoing search for these megastructures continues to inspire scientific research and the quest to understand the cosmos.