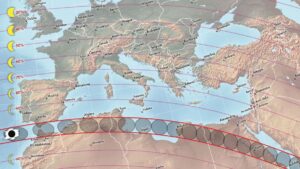
A geologist collects magma samples in a field campaign over the Tibetan Plateau. Credit: Hu Fangyang
For years, scientists believed that changes in Earth’s interior, such as volcanic eruptions and collisions of tectonic plates, primarily affected the surface environment. Events such as the mass extinction around 66 million years ago and the transitions between glacial and greenhouse climates are believed to be mainly due to these deep Earth processes. However, a new study published in Nature Communications revealed a surprising new aspect: solar radiation can also affect Earth’s deep interior.
Solar radiation varies with latitude, creating temperature gradients at the sea surface that affect the distribution of marine life. These carbon-rich organisms are transported into the Earth’s interior by subduction of oceanic plates. Researchers from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have found that this process significantly affects the redox state of the arc magma.
The “redox” state of arc magma refers to the balance between reducing (loss of oxygen or gain of electrons) and oxidizing (gain of oxygen or loss of electrons) conditions in the magma formed in volcanic arcs. Marine organisms serve as organic carbon and act as the primary reducer for the solid Earth. Therefore, the redox state of arc magma may reflect how the influence of the sun penetrates deep into the Earth.
Thousands of magma samples were collected to reveal global variations in redox state that are critical for targeting metallic ores such as copper, tin and lithium, key elements for renewable energy technologies. These samples provided remarkable insight into interactions between surface climate and deep Earth processes.
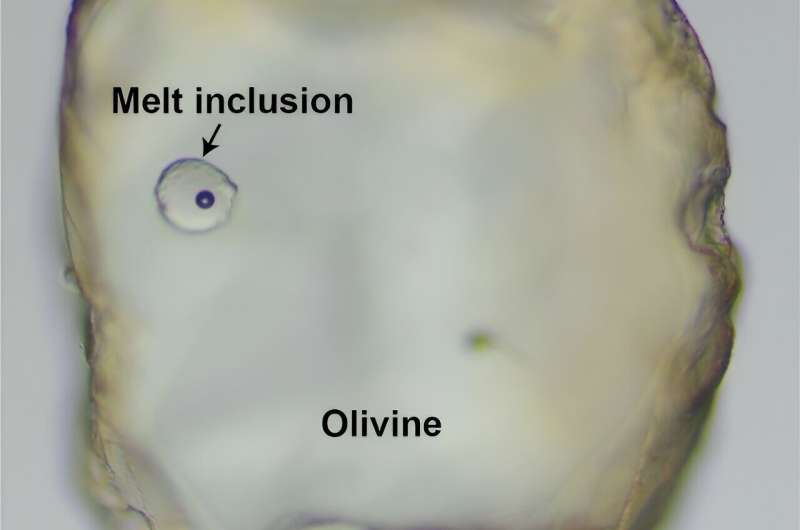
Olivine-bearing melt inclusions. Credit: Chinese Academy of Sciences
The levels of vanadium and scandium in the arc magma served as key indicators in the geochemical models. By compiling global geochemical data from Cenozoic arc magma and olivine-bearing melt inclusions, the researchers found a latitude-dependent redox distribution of arc magma with less oxidized magma at lower latitudes compared to those at higher latitudes. widths.
“Previous studies mainly compared samples from the same longitudinal regions, such as the United States in the northern hemisphere and Mexico in the tropical zone, without finding significant differences. However, our samples from different latitudes showed different redox reactions, which piqued our curiosity. Trying to explain these differences led us to find this unexpected pattern,” said Wang Bo, a geologist and co-author of the study.
“This unexpected pattern suggests that surface climate has a direct influence on the deep Earth. It also suggests that the Earth’s surface environment and climate have a vital influence on the Earth’s depths,” WAN said.
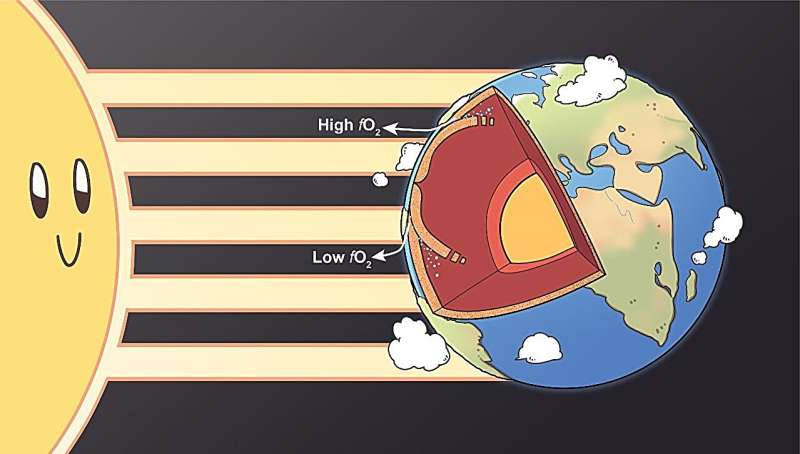
The influence of the sun on the earth’s interior. Credit: Chinese Academy of Sciences
So how does the sun work on Earth’s interior?
Additional evidence comes from seafloor surveys showing reduced carbon deposition at lower latitudes. This carbon interacts with sulfur to form sulfide, which is then transported into the mantle, contributing to the observed redox pattern.
“The observed pattern suggests a strong connection between the surface environment and the redox state of the deep Earth, providing new directions for investigating the resources and environmental impacts of subduction systems at different latitudes,” said Hu Fangyang, corresponding author of the study.
Although the results are compelling, the researchers acknowledge the need for more extensive data from global marine and subducted sediments. The study opens up new avenues for research.
More info:
Fangyang Hu et al, Latitude-dependent fugacity of oxygen in arc magmas, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50337-6
Courtesy of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Quote: Scientists say sun’s influence penetrates deep into Earth (2024, July 23) retrieved July 24, 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-07-scientists-sun-penetrates-deep- earth.html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for any fair dealing for the purposes of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.